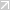Organic Layer
Highland Deciduous Woodlands
Wetlands Studies
Impact of Permafrost Degradation on Ecosystems
Wetlands and Their Importance for Plant Growth
Permafrost Thaw Impacts
Riparian Mixed Forests
Ecosystem Functions and Tundra Biodiversity
Wetlands and Their Contributions to Carbon Sequestration 
Bogs are acidic wetlands with a thick
layer of peat, and fens are nutrient-rich wetlands fed by groundwater
...Wetlands are highly effective at sequestering carbon due to their waterlogged conditions, which slow down the decomposition of
organic matter
...
Highland Deciduous Woodlands 
The forest floor is covered with a
layer of leaf litter, which serves as a rich source of nutrients for the soil and supports a diverse array of decomposers
...Fungi play a crucial role in decomposing
organic matter and recycling nutrients, contributing to the overall health of the woodland ecosystem
...
Wetlands Studies 
Wetlands are typically rich in
organic matter, which contributes to their high productivity
...Bogs Acidic wetlands with waterlogged soils and a characteristic
layer of peat moss
...
Impact of Permafrost Degradation on Ecosystems 
Overview Permafrost is a
layer of soil, rock, or sediment that remains frozen for two or more consecutive years
...Some of the key impacts include: Release of greenhouse gases: As permafrost thaws, the
organic matter within it decomposes, releasing carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere
...
Wetlands and Their Importance for Plant Growth 
Bogs Acidic wetlands with a thick
layer of peat and specialized plant species like sphagnum moss
...Carbon Sequestration: Wetlands are important carbon sinks, storing large amounts of carbon in the form of
organic matter, which can promote plant growth
...
Permafrost Thaw Impacts 
Permafrost is a
layer of soil, rock, or sediment that remains frozen for at least two consecutive years
...Some of the key impacts include: Release of greenhouse gases: As permafrost thaws,
organic matter that has been frozen for thousands of years begins to decompose, releasing carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere
...
Riparian Mixed Forests 
The soil in riparian forests is often nutrient-rich due to the periodic flooding that deposits sediments and
organic matter
...These forests typically consist of a mix of deciduous and evergreen tree species, creating a diverse canopy
layer ...
Ecosystem Functions and Tundra Biodiversity 
One of the defining features of tundras is permafrost, a
layer of permanently frozen soil that restricts the growth of plant roots
...Nutrient cycling: The cold and wet conditions in tundras slow down the decomposition process, leading to the accumulation of
organic matter that enriches the soil
...
Wetlands in Water Filtration 
vegetation in wetlands helps to trap and absorb pollutants such as heavy metals, excess nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus, and
organic matter
...Bogs Bogs are acidic wetlands that are often covered in a thick
layer of peat moss
...
Northern Pine Forests 
The forest floor is often covered in a thick
layer of
organic material, known as duff, which helps to insulate the soil and provide nutrients for plant growth
...
Start mit Franchise ohne Eigenkapital 
Der Weg zum Franchise beginnt mit der Auswahl der Geschäftsidee, d.h. des passenden Franchise-Unternehmen. Ein gute Geschäftsidee läuft immer wie von selbst - ob mit oder ohne Kapitial. Der Franchise-Markt bietet heute immer neues so auch Franchise ohne Eigenkapital...